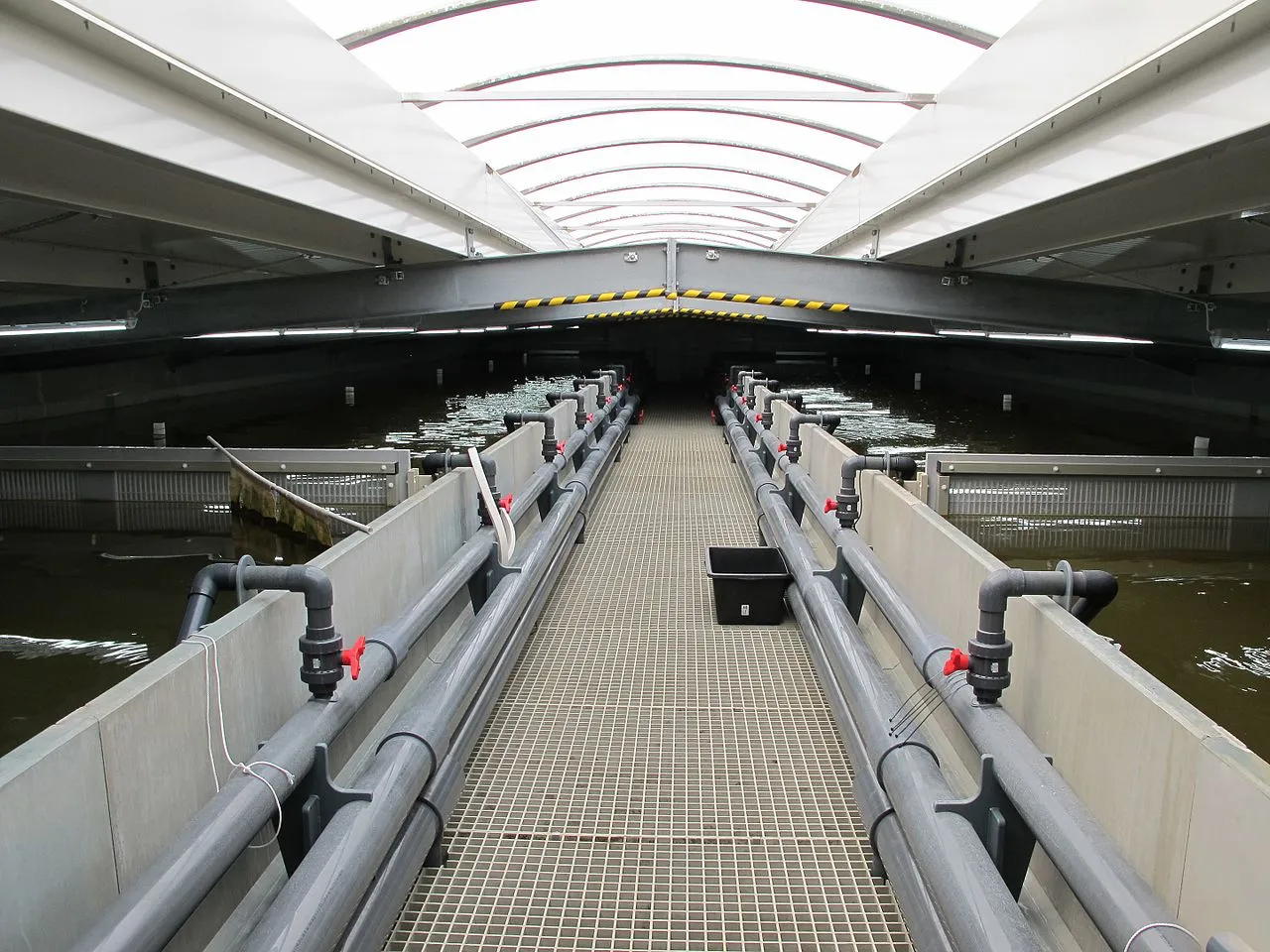
Indoor shrimp farming is a method of farming shrimp in controlled indoor environments rather than traditional outdoor ponds or coastal areas. It has gained popularity as a way to produce high-quality, fresh shrimp in practically any location. Here are some key points about indoor shrimp farming:
Types of Indoor Shrimp Farming Systems:
Indoor shrimp farming typically utilizes two main types of systems:
- Clear Water Systems: In these systems, shrimp are grown in tanks with filtered and treated water, maintaining optimal water quality for shrimp growth.
- Hybrid Biofloc Systems: These systems incorporate the use of beneficial bacteria to convert waste products into a biofloc, which provides a food source for the shrimp and helps maintain water quality.
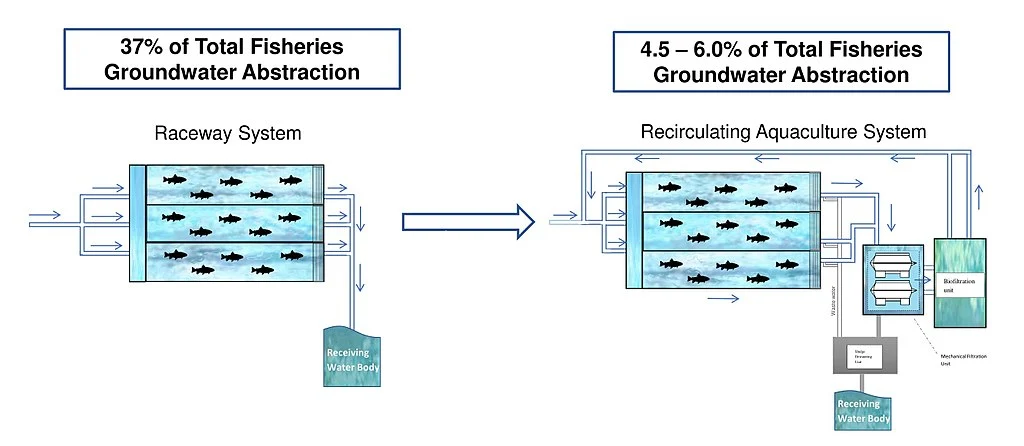
Benefits of Indoor Shrimp Farming:
- Controlled Environment: Indoor shrimp farming allows for precise control over water quality, temperature, and other environmental factors. Which relates to improved shrimp growth and health.
- Year-Round Production: Unlike traditional outdoor farming, indoor systems can operate year-round, providing a consistent supply of shrimp.
- Location Flexibility: Indoor shrimp farms can be established in various locations, including landlocked areas, making it possible to bring shrimp farming closer to consumer markets.
- Sustainability: Minimizes environmental impacts, such as reducing water usage and preventing pollution.
Big Plans for UK’s Land Ocean Farm

Land Ocean Farm is a start-up company that plans to establish a land-based indoor shrimp farm in the UK. The company aims to grow whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in a biosecure, land-based recirculating aquaculture system (RAS). Aiming to produce 1,000 metric tons (MT) of shrimp per year.
The company is actively fundraising to finance the first stage and hopes to start construction in early 2024 at a site in Cheltenham, Gloucestershire, UK, with the hope of building an initial unit to grow 100 MT of shrimp. Then later down the line, adding additional modules to reach full production in future phases of growth.
Eventually, Land Ocean Farm plans to partner with farmers looking to diversify their income. Ultimately to build satellite production units and enhance the company’s plans as well. According to intrafish, land ocean farm is still in early stages of development and raising funds.
4 Challenges for land ocean farm
- Funding: Land Ocean Farm is actively fundraising to finance the first stage of their indoor shrimp farm project. Securing funding can be a challenge, and the project may depend on their ability to secure adequate funding.
- Technology and Infrastructure: Building and operating an indoor shrimp farm requires specialized technology and infrastructure. Land Ocean Farm has partnered with world-leading aquaculture experts to establish the technology for shrimp aquaculture. However, there may be challenges in implementing and maintaining this technology and infrastructure.
- Market Demand: While there is a growing demand for sustainable and locally produced seafood, meeting that demand is another thing entirely. As a start-up, they may face challenges in establishing a customer base and competing with established seafood producers.
- Market Positioning: With the presence of established shrimp farming operations, Land Ocean Farm may face challenges in positioning themselves in the market and differentiating their product. They would need to develop a unique selling proposition. Then effectively communicate the value of their sustainably produced shrimp to attract customers.
Environmental Impact
Land Ocean Farm’s indoor shrimp farming has the potential to minimize environmental impacts compared to traditional outdoor shrimp farming.
- Water Pollution: Shrimp farming can produce organic waste, chemicals, and antibiotics, which can pollute groundwater or coastal estuaries. However, shrimp aquaculture is designed to minimize water usage and prevent pollution. Using recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) that treat and reuse water, helps with this.
- Habitat Loss: Traditional shrimp farming can lead to habitat loss in salt flats, mudflats, estuaries, tidal basins, and coastal marshes. These are essential habitats for many coastal species. However, this biosecure farm method can be established in various locations, including landlocked areas, minimizing the need for coastal habitat.
- Biodiversity Loss: Shrimp farming can compete for food and habitat with natural populations, jeopardizing the integrity of ecosystems. However, shrimp aquaculture can be designed to minimize impacts on natural populations by using closed systems that prevent escapes and reduce the risk of disease transmission.
Looking to the Future
Despite the challenges that the company may face, their indoor shrimp farming has the potential to minimize environmental impacts. Sustainable practices, minimizing water usage and preventing pollution, are the main focus of indoor shrimp farming. This type of shrimp aquaculture is a more environmentally friendly approach to shrimp production.
The world can benefit from Land Ocean Farm’s indoor shrimp farming in several ways. First, indoor shrimp farming can provide a consistent supply of fresh, high-quality shrimp year-round, reducing reliance on wild-caught seafood. Second, it can be established in various locations. Landlocked areas are an option as well, making it possible to bring shrimp farming closer to consumer markets. Third, the design minimizes environmental impacts, such as reducing water usage and preventing pollution, contributing to sustainable seafood production.
Overall, Land Ocean Farm has the potential to address the challenges of traditional outdoor shrimp farming. Simultaneously providing a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to shrimp production. By embracing innovative solutions, we can grow better shrimp more effectively. We can meet the growing demand for seafood while minimizing environmental impacts.
Discover more from The Oyster Encyclopedia
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

